
Laser rangefinders are indispensable measurement tools having a wide range of applications in various sectors like sports, construction, forestry, and tourism. This tool is handy but if you don’t know How does a laser rangefinder work works in different conditions, you won’t be able to get the best out of it. Little error in the positioning or handling can lead to a big flaw in the final value.
By understanding the functioning and basic principles of the laser rangefinder you can use them in a more skillful way on the field. In this guide, I’ll discuss how a laser rangefinder takes measurements, how you interpret these measurements, and how different factors affect the working of a laser rangefinder. If you need good and quality Bushnell rangefinder binoculars click on the link.
Table of Contents
How Does a Laser Rangefinder Work | Everything You Need To Know
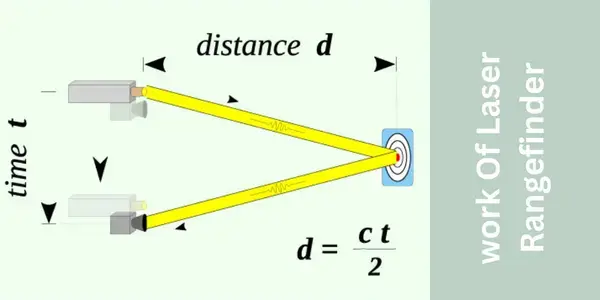
A laser rangefinder is a device that we use to measure the distance of distant objects from a specific point. Laser rangefinders use a laser beam that is aimed at distant objects. This laser beam hits the target and is reflected back to the screen of the laser rangefinder. The tool uses a high-speed time-measuring clock that records the time the laser beam has taken from the point it left the device until it returned.
Optics
It makes sense to start the discussion with optics as the rangefinder’s ability to see the targets depends upon the quality of optics. Professional-grade laser rangefinders use high-quality optics with higher magnification to range the targets in a given field. Optics have nothing to do with distance measuring or data processing of the device but still, they are an essential part.
The magnifying power of the optics allows you to see the far-distant smaller targets. After finding the targets, you can hit the laser beam and measure the distance through the device. The magnification of the optics used in standard rangefinders is between 5x to 10X. The working range of the laser rangefinder mainly depends upon the range of the optics it uses.
The higher magnification allows you to see a more detailed picture of your targets. Also, you may miss some of your targets in the field if the magnification power of the optics is not up to the mark. I compared the two rangefinders with 5x and 10x magnification to see how it affects the laser rangefinder’s working ability.
There were 3 to 4 targets in the fields that were missed by 5x optics and detected by 10x optics. The optics in a rangefinder are also known as rangefinder binoculars. The working of these binoculars is the same as the regular binoculars. You need to focus on the binoculars with the help of eyecups.
Rangefinder Lasers
Lasers are of course the core components of laser rangefinders. It is like the measuring tape of the device. The laser beam leaves the device, pins the target object, and then reflects back to the device. A rangefinder emits multiple laser beams at a single time. The final measurement doesn’t depend upon the traveling history of a single laser beam.
Instead, it is a series of beams that hit the target, reflect back and a series of readings are recorded in succession. If you wonder why a rangefinder sends a series of laser beams, consider this example: When we are in the field there are various other objects along with our target object. For instance, we want to target something that is somewhere behind the branches. When we send a laser beam it will be partially blocked by the tree branches.
The remaining part will hit the target. The device will measure the travel time and analyze the data of different beams in the series. You will have to interpret the final results to finish out the original distance of the object. Laser rangefinders use different types of laser techniques and therefore the functioning of one laser rangefinder may be different from the other.
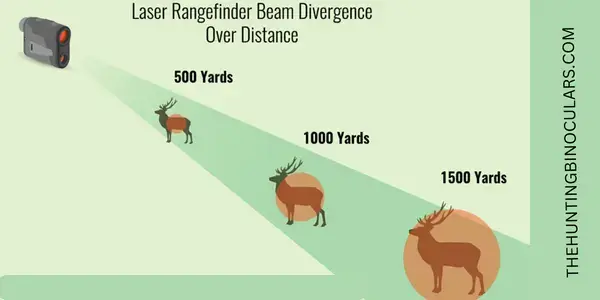
What Is Laser Beam Divergence
The “beam divergence” is an important phenomenon in laser measurement devices. The rangefinder’s ability to get the laser energy on target or produce a well-focused beam is directly linked with the beam divergence. It is the angular measurement of how focused the laser beam is. The smaller beam divergence means a more focused beam and better accuracy and ranging precision.
Beam divergence is not the only parameter to judge the ranging accuracy of a rangefinder. However, it is a crucial factor and the effect of beam divergence intensifies as the target gets smaller and farther. The laser beam spreads out as it leaves the laser pointer from the device and beam divergence is the measurement of how much it spread apart. The higher divergence makes it easier to aim at your target in the field.
However, it may lead to ambiguous results and measurements as the spreading beams are likely to hit multiple objects in the field. It can be a little hard to interpret the desired results. A tight laser beam with limited convergence will help you get more precise results but it can be a little hard to target the desired objects in the field. You must be skilled enough to get a perfect aim and focus on the object in the field.
Rangefinder Software
The software of the rangefinder is the controlling part of the device. The software of the rangefinder collects and processes the data, compiles the results, and analyzes the results to help you get the desired value in the end. Smart laser rangefinder uses more advanced and powerful software and the range precision of these devices is more than impressive. The standard rangefinder is rather simple and their software displays the first result measured by the device.
The advanced rangefinder uses multi-pulse technology and sends a series of laser beams at a single time. The rangefinder receives a series of reflected beams. Advanced software is smart enough to identify the target object and ignore the outliers like trees, bushes, etc. Here are the most common ways through which laser rangefinder software interprets the results:
Closest Cluster
In this method, the software considers the cluster of beams that has been reflected from the object that is closest to you. This is not preferred for hunting and forestry. Consider the example of the game hiding behind the bushes. Since bushes are closer to you than the target game, you will get the results for bushes and not for the game.
Most Centered Cluster
In this method, the software will present you with the distance calculated by the most centered cluster readings. This is one of the most accurate methods as the laser beam is most likely to be centered on the desired object in all conditions.
The Farthest Reading
The furthest reading works like the closest cluster. The software considers the reflected beams coming from the farthest object and presents you with the final result. The accuracy of this method depends upon the field conditions. The accuracy level of the software interpretation method is different. Some methods are more useful in one situation than the other.
For instance, the closest measurement distance is simpler than the most centered cluster method and offers better accuracy in construction site applications. However, most centered cluster methods are more useful in applications like forestry, hunting, and golf, where the field is crowded with more outliners.
Binoculars With Selective Targeting Systems
In standard laser rangefinders, you can’t control how your software interprets the data. However, rangefinders with selective targeting features use advanced software that allows you to select the interpretation mode. Depending upon the field conditions, and application requirements you can select the data interpretation or data analyzing mode of the software.
Angle Range Compensation
Angle range compensation is another part of the laser rangefinder software. The angle compensation comes in handy when you want to measure the distance of the objects that are not on the same level as you. For instance, you want to measure the distance of an object uphill or downhill. The angle compensation will automatically detect the difference in angle and help you get the correct measurement in the end.
Pulse Laser Rangefinders vs phase Laser Rangefinders
Depending On the data processing and distance calculation methods there are two types of LRFs: Pulse LRF and Phase LRF. Phase LRF measures the travel time of the reflected beam in two planes based on the phase. The LRFs system measures the Phase delay of reflected and emitted laser beams. On the other hand pulse rangefinder simply records the travel time of the pulse that has been emitted by the laser and reflected by the object. The software uses this travel time to measure the distance of the target objects.
Here is a brief description of the important attributes you must know to understand the functioning of laser rangefinders:
Accuracy
Measurement accuracy refers to how close a particular rangefinder can measure to the original value. The measurement accuracy of the rangefinders is 5mm. However, advanced laser rangefinders with selective target systems and fast digital clocks let you measure the distance of the object with an accuracy of 1mm or 2mm.
Operating Range
The operating range of the LRF is a range in which it can measure the distance of objects. Laser rangefinders are designed for different applications like hunting, golf, forestry, tourism, and construction. For hunting, forestry, and golf you will need LRF with a higher operating range.
For construction site applications an LRF with a shorter operating range will also work. Standard LRFs come with an operating range of 40-90 meters. LRFs designed for sports like hunting and golf can operate within a range of 120-250 meters. Long-range laser rangefinders can measure the distance of objects located as far as 1500 meters.
Aperture Size Of The Optics
The aperture size of the optics is another crucial feature that affects the functioning and accuracy of the rangefinder. The aperture is part of the device through which the reflected laser beam enters the device. The larger aperture allows more beams to enter. The larger aperture allows the device to collect more data and generate more precise results.
Laser Dot Diameter
Laser dot diameter will affect your ability to find and aim at the target in your field. The diameter of the laser dot varies between 6 mm to 60 mm. If you want to aim the objects that are located close to you you will need a smaller laser diameter. However, for far-distant objects, you need to work with a bigger laser dot.
FAQs
Are laser rangefinders worth it?
The laser rangefinder is worth it if you want to improve your game performance or improve your work accuracy in construction. Laser rangefinders have impressive accuracy and come at a wide range of prices allowing you to bring professional-grade efficiency to your work and games.
How do you aim for a laser rangefinder?
You aim for a laser rangefinder by looking through the eyepiece. Focus your eyepiece and set the magnification according to the size and distance of the object. Now place your crosshair on the target object and hold the device steadily and briefly. Now press the power button on the top. Make sure you keep the rangefinder intact while pressing the power button.
How do rangefinders work hunting?
Laser rangefinders work hunting as they allow you to target your game in the field and measure its distance. You can see your target through the optics on the laser angle finder while the laser beam allows you to measure the distance.
Do rangefinders work in fog?
Not all rangefinders work in fog since a dense fog can drastically disperse the laser beam. However, advanced laser rangefinders use rain or fog mode. It allows you to reduce stronger and more focused beams. However, you can’t expect accurate results as fog and rain have a dramatic impact on the functioning of rangefinders.
Conclusion
Though the basic working principle is the same for all laser beams, their functioning, accuracy, and ease of use depend upon the quality of the hardware and software it uses. Advanced LRFs use software that interprets the most accurate result automatically. Also, the accuracy of results depends upon your skill level and the quality of optics and conditions in the field.
